Mommy's Thumb(De Quervain’s tenosynovitis), the cause, symptoms and treatment
Mommy‘s Thumb: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Reviewed By Doctors of Asia Medical Specialists
(Last updated on: January 21st 2021)
Mommy’s thumb is a common urban-associated disease (UAD). The medical term is de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, also known as de Quervain's syndrome. Since this condition is usually referred to as mommy's thumb, it is mistaken for a disease only associates with mothers or housewives. Indeed, the high-risk group is not limited to women. The following are the high-risk groups for mommy’s thumb.
High-risk groups for mommy’s thumb:
New parents |
Housewives |  Individuals who use mobile phones or tablets for a lengthy time |
 Individuals who knit or sew for a prolonged time |  Golfers |  Desk jockeys |
 Waiters/waitresses |  |  |
A common characteristic is found among the high-risk individuals, which they tend to overuse the wrist chronically. For example, parents of the newborn would use their hands or wrists to support the baby’s head when breastfeeding and bathing for a prolonged time; office staffs would use keyboard and mouse for a prolonged time; hairstylists would constantly use the scissor, and waiters/waitresses in restaurants also have a greater chance of suffering from mommy’s thumb as they often keep going back and forth between the kitchen and the guests' table holding several dinner plates. Finally, e-sports players that gone viral in the past decade also have a higher chance of suffering from the disease because of the chronic excessive use of their fingers and wrists.
In addition to the above high-risk groups, individuals who use mobile phones for a prolonged time also triggers mommy’s thumb. Since mobile phone screens are getting larger nowadays, and we get used to using them with one hand. Under such circumstance, the burden on our thumb increases. Finally, mommy thumb may be related to pregnancy as well.
Causes of Mommy’s Thumb
The exact cause of mommy’s thumb is unknown, but many people believe that chronic overuse and activities involved repetitive radial and ulnar wrist motion may contribute to the underlying tendinopathy.
Symptoms of Mommy’s Thumb
Generally, the symptoms of de Quervain's tenosynovitis are easy to detect. Patients may feel pain on the side of the wrist near thebase of the thumb, and when flexing the thumb, twisting the wrist, making a fist, or grasping, the tendon tightens and the pain increases. There is also swelling of the wrist near the base of the thumb. If ignored and treated inappropriately, the pain could progress to the entire thumb or the forearm. Daily activities and work-life of the patient will be affected as well. For example, movements like twisting a towel, holding a mobile phone with one hand, typing, using a mouse or even holding a shopping bag will also be painful. These symptoms are most obvious in the morning, and pain will significantly reduce after a period of activity. Yet it will worsen again if the patient continues to repeat some thumb/wrist movements.
Mommy’s thumb self-assessment
If you want to check whether you have a mommy’s thumb, you could place your thumb in your palm then make a fist, and extend your wrist to the forefinger. If the wrist near the base of the thumb is painful, you may suffer from inflammation. Please see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
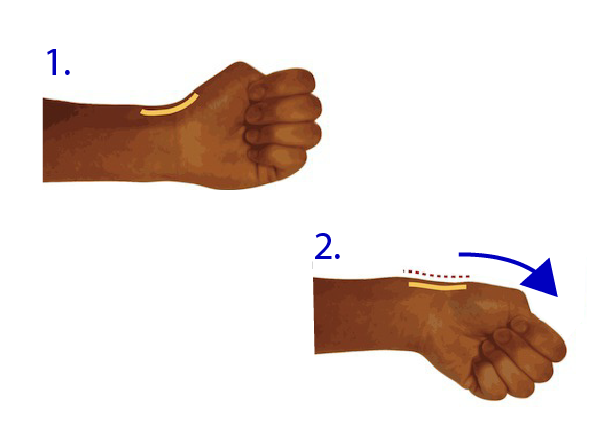 |
Treatments for mommy’s thumb
Treatments aim at eliminating inflammation and smoothening pain, which include:
- Avoid repeated wrist/thumb movements as much as possible to rest the inflamed area
- If swelling occurs, try ice compression to reduce the symptom
- Medication: A single steroid injection could effectively reduce more than 80% of the symptoms, and over half of the patients remained symptom-free for at least 12 months.
- Physiotherapy or occupational therapy: The therapist will evaluate the patient symptoms and make suitable recommendations, including muscles strengthening and pain relief exercises.
- Surgical treatment: If all the above methods fail to improve the patient's condition, surgery may be the last option. The doctor will loosen the inflamed tendon sheath so that the tendon can resume normal activities and relieve the pain.
- The doctor will first make an incision along the thumb near the wrist and then look for the inflamed tendon sheath
- Make another incision along the top of the tendon sheath to make room to release the pressure of the tendon and restore normal sliding
- Finally the doctor will sew the skin and wrap the wound with thicker boil
Prevention is better than cure
To avoid suffering from mommy’s thumb, its important to take prevention measures proactively. In addition to avoiding excessive and repeated use of the thumb, you may also perform soothing exercises from time to time to stretch related tendons.
- Exercise 1:
- Put your hands on the table, with your palms facing up. Lift the thumb and forefinger, and gently press the tip of the forefinger with the tip of the thumb to stretch the base of the thumb and wrist.
- Hold the action for 6 seconds then relax, repeat 10 times.
- Exercise 2:
- Extend your arm and make a handshake, bend your thumb to your palm. Use the other hand to gently extend the thumb and wrist downwards, so that the wrist is stretched near the thumb.
- Hold the movement for 15 to 30 seconds then relax, repeat 2 to 4 times.
*Remarks for stretching: Keep the movement steady, slow and smooth when stretching, and don't shake the stretched part or overstretch.


